
There are many contraceptive methods available in the market. Deciding which means to use may be difficult because there are many factors to consider, including costs, future pregnancy plans, side effects, and more. Most methods are quite effective if used properly. In principle, the best method is one that you use consistently, will be acceptable to you and your partner and does not cause annoying side effects.
There are a large number of contraceptive methods on the market, the most popular are the combined contraceptive pills and condoms.
Some contraceptives, such as intrauterine devices (IDUs) and injections, have a low risk of failure because they are not dependent on how they are being used.
In general, contraception intended for use around the time of the intercourse (such as a condom or diaphragm) are generally considered less effective than other methods. If you forget to use contraception or your contraceptive fails, it is possible to reduce the risk of pregnancy, up to 5 days after the intercourse, using the “morning after” pill (up to 72 hours), or inserting an IUD device.
Selection of contraceptives
It may be difficult for you to decide which contraceptive method is best for you, even only because of the wide variety of options available today. In principle, the best method is the one you use consistently, will be acceptable to you and your partner, and does not cause annoying side effects.
Other factors to consider:
- How effective is the method?
- Is it convenient for me? Will I remember to use it?
- Is this a reversible method? How fast can I conceive after stopping it?
- Will this method cause me to bleed more or less during menstruation?
- Are there side effects or possible complications?
- Is it a reasonable price for me?
- Does this method protect against sexually transmitted diseases?
Keep in mind that there is no perfect method. You may want to consider the pros and cons of each method, and choose the one that best suits you.
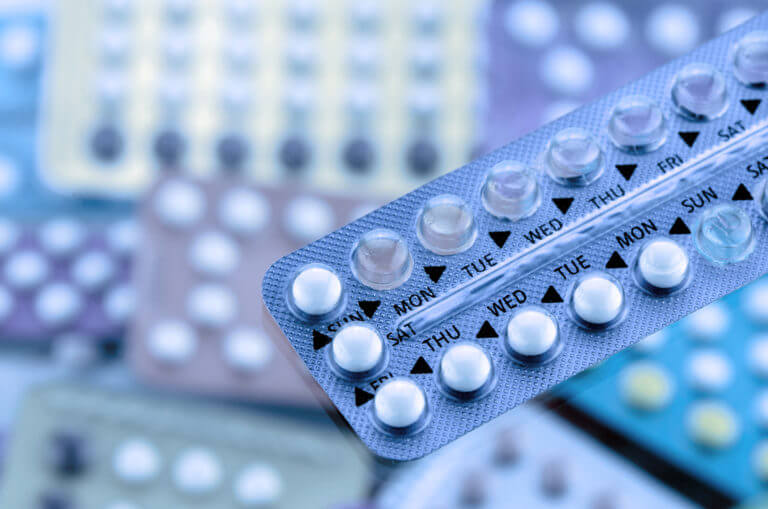
Contraceptive pills (OCP)
Most pills contain a combination of the two female hormones – esrogen and progesterone. The pill creates a pregnancy-like condition in the body and prevents ovulation. The benefits of the pill are: excellent pregnancy prevention, reduction of menstrual bleeding, reduction of menstrual pain, reduction of premenstrual effects, and prolonged administration also reduced the risk of ovarian and uterine cancer. Possible side effects of the pill include: nausea, chest congestion, mood swings, migraines, fluid retention (no weight gain!) And more.
Irregular vaginal bleeding is especially common during the first months of use, or if you forget to take a pill.
The most serious side effect of pills is the formation of blood clots in the body, and is extremely rare, in the range of 1: 5,000 – 1: 10,000 patients using the pill. Your doctor should make sure you do not have any known risk factors for coagulation, prior to starting treatment.
Progestin pills only
Unlike the usual pills, there are also progestogen pills without estrogen, also called mini-pill. This type of pill is especially useful for women who are breast feeding or have a risk or a ban on estrogen therapy. Progestin-only pills are as effective as combined pills if they are taken at the same time every day.
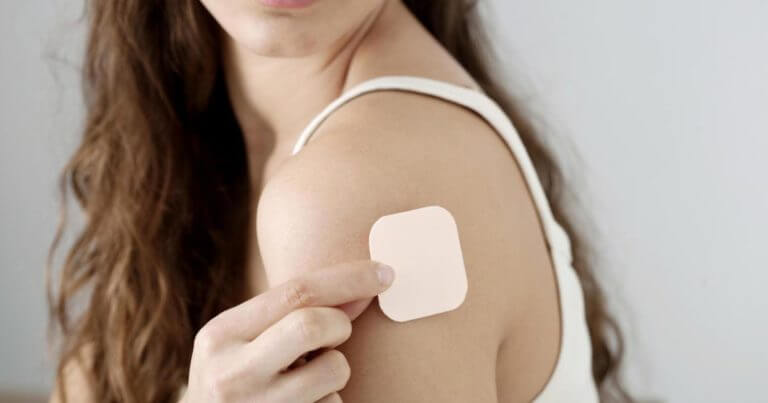
Patches
Marketed as EVRA. This is actually identical to pills, but does not go through the digestive system. The patch is placed for a week on the arm, shoulders, upper back or hip, in three cycles, and in the fourth week you stop for menstruation. Then a new round begins. The risks and side effects of the patch are similar to those of a pill, but there may also be local sensitization to the skin. The advantage of the patch is that it is unnecessary to take it every day, and have no digestive side effects.
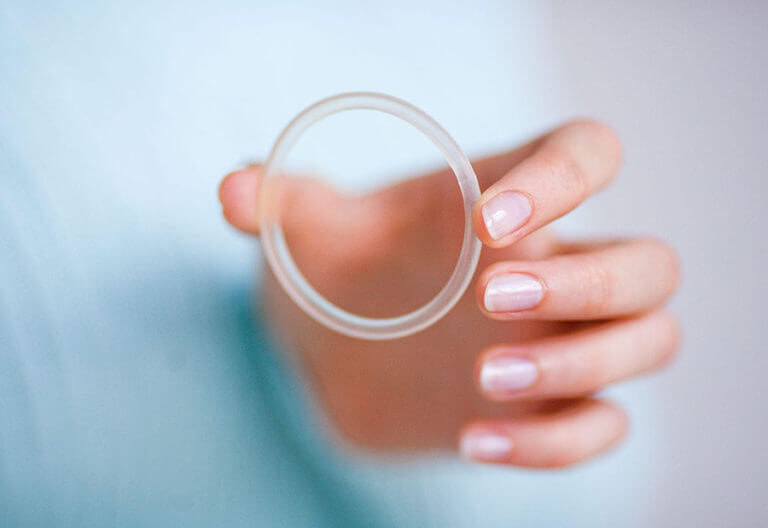
Nuvaring® vaginal Ring
A vaginal ring is a gentle, flexible plastic ring containing estrogen and progestin. The ring is inserted by yourself, into your vagina and stays there for 3 weeks. In the fourth week it will be taken out and you will get period. The ring is not felt, easy to insert and remove. The ring works in the same mechanism of combined pills and has the same side effects. The benefits of the ring are that it does not need to be taken daily, so hormone levels are more stable in the blood, which reduces the risk of irregular bleeding. Also, no digestive side effects.

Progesterone injections
(Medroxyprogesterone Acetate or Depo-Provera)
It is a long-acting progestin hormone. It is administered by injection once every 3 months and is very effective in preventing pregnancy. Following the injection there will be no periods for the duration of use.
Side effects: The most common are irregular or prolonged bleeding, especially during the first months of treatment. Delayed recurrence of periods, for up to 9 months from the last injection, is possible.
Blocking devices
Contraceptives that block the sperm from reaching the womb include condom and a diaphragm.
Male condom – This is a thin, flexible sheath placed on the penis. To be effective, must put it in the right timing. Condoms are more effective in using spermicide in the vagina. In general, condoms are not a reliable contraceptive. Condoms, on the other hand, are effective in preventing the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases (except for the Papilloma virus), and are therefore recommended for use in combination with hormonal or other contraceptives.
Diaphragm – a device made of latex, rubber or silicone, which exists in a number of sizes and requires adjustment by the treating gynaecologist. These devices must be used with spermicide, inserted prior to intercourse, and should be left in the vagina for six to eight hours after intercourse.
Spermicides
These are chemicals that destroy the sperm. They are available in most drugstores without prescription. They are available in a variety of forms including gel, foam, and cream and are recommended for use along with any blocking contraception.
IUD devices
A uterine-fitting device inserted by a gynaecologist through the vagina and cervix into the uterus. Very convenient and very effective. In general, there are two types of devices – copper and hormonal.
The copper IUD devices are effective for 5 to 10 years and contain no hormones. In some women, menstrual bleeding and menstrual pain will increase.
Mirena – A device similar in form to the copper device, but also contains a slow-release levonorgestrel progesterone. In addition to its effectiveness as a contraceptive device, progesterone causes thickening of the cervical mucus, endometrial lining thinning, and a slight effect of suppression of the ovaries. As a result of the above, the efficiency of the device is excellent as a contraceptive, and another advantage of it, is a significant reduction in menstrual bleeding and menstrual pain. It is effective for 5 years.
A smaller model called Kyleena which is designed for teenagers and pre pregnant women is pretty similar to the Mirena but contains less progesterone.
Sterilization
Sterilization is a procedure that prevents you or your partner from being fertile permanently. In women it is performed by ligation of the fallopian tubes, and in men by ligation of the semen duct. Sterilization is permanent, and should be performed only after discussion of all existing contraceptives in the market and future birth plans.
Tubal ligation – A procedure in which the two fallopian tubes are disconnected, cut off or diathermied, and the passage of oocytes from the ovaries into the uterus is prevented. Can be done during cesarean section or by laparoscopy.
ESSURE is a simple method for blocking the fallopian tubes hysteroscopically, through the vagina without the need for abdominal surgery. In the procedure a tiny coil is inserted into the fallopian tubes with a hysteroscope (a small camera inserted into the womb). The tissue within the fallopian tubes grows into the coil, and within 3 months they are blocked. The operation can be performed with or without anesthesia, as part of a day procedure. In the first three months, additional contraceptives should be used.
Ligation of the semen duct – Sterilization in men is performed by ligatng the semen duct. This is a safe, very effective procedure that can be performed under local anesthesia. Following the ligation, you must wait 3 months for the entire existing sperm stock to run out. Therefore, another contraceptive method should be used until the sperm is examined. The ligation does not effect erection, testosteron levels or has any other side effects.
Other contraceptives
Some couples choose not to use the above-mentioned methods due to religious or cultural reasons.
Safe days – a method based on physiological changes during menstruation. The method relies on identifying the fertile days of the cycle. The woman must identify physical manifestations of ovulation, such as changes in the cervical secretion, body temperature, and avoid intercourse during these days. The method is not safe, and is suitable for women with a regular and precise cycle only.
ggg
FAQs
What is a contraceptive?
Contraceptives are any method used to prevent pregnancy. There are multiple methods that varied in their reliability, safety, possible side effects, easiness of use, permanent or temporary. The options include: safe days, condoms, diaphragm, contraception pill, Implanon, intra-uterine device (Mirena, Kyleena, copper IUD), progesterone injections, tubal ligation, vasectomy.
How does the contraceptive pill work?
Most pills contain a combination of the two female hormones – estrogen and progesterone. The pill creates a pregnancy-like condition in the body and prevents ovulation.
What are contraceptive pills?
Most pills contain a combination of the two female hormones – estrogen and progesterone but some contain only progesterone. The pill creates a pregnancy-like condition in the body and prevents ovulation.
Can contraceptive injection cause infertility?
No, the progesterone injections are not causing infertility but it can take a while for the periods to resume after the injection. The injection protects from pregnancy and planned to stop periods for 3 months’, but it is well known that it can take up to 9 months’ for the periods to resume in some women.
Can contraceptive pills cause weight gain?
Yes, but relatively few women suffer from weight gain on hormonal contraceptives. It is unpredictable which contraceptive will cause weight gain in which women. You’ll need to try and see how it affects you.

