
What is an ovarian cyst?
An ovarian cyst is a general term for a large number of conditions, in which there is some tumour on or within the ovaries. The tumour may be benign or malignant, liquid or solid, isolated or part of the process of disease spread in the pelvis and so on…
In most cases, the woman will not even know about the existence of the cyst. But, in some situations, even a benign cyst can cause pain, stress, and changes in the menstrual cycle.
In addition, a cyst can cause various complications, such as when it ruptures and causes its contents to be spilled into the abdominal cavity, or twists the ovary, blocking its blood supply and possible loss of the ovary (ovarian torsion)
Most cysts are benign and require only follow-up. For example, every woman has a functional “cyst” that is the follicle that grows every month and ovulates.
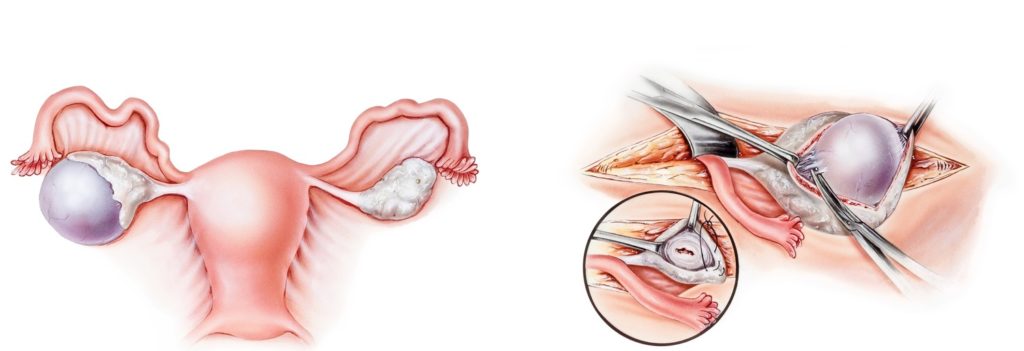
Ovarian cyst symptoms
Cysts are present in women of all ages, but especially at the age of fertility.
Diagnosis and follow-up of the cyst are done by gynecological ultrasound, which allows determining the type of the cyst, its size, whether it contains irregular blood flow, its complexity, and other findings such as ascites, additional masses, enlarged lymph nodes…
There are also some more specific and less specific markers for different ovarian tumors, which can be tested in blood tests.
The need for surgical treatment of the cyst will be determined according to: symptoms (abdominal pain, pressure on the abdominal organs, etc.), cyst type, cyst size and growth, woman’s age, risk factors in the background and other findings in the abdomen and pelvic, and the blood tumor markers.
Most surgeries for ovarian cysts are performed in a laparoscopic approach (see Laparoscopic Surgery), which are relatively easy with rapid recovery.
Benign cysts
Benign cysts are the most common in childbearing age and include:
Corpus Luteum
A “yellow body” – the cyst from which ovulation originates. A cyst that has a typical ultrasound appearance and is usually not felt by the woman, may rupture and cause abdominal bleeding, or cause ovarian torsion.
Dermoid cyst
a benign cyst with a complex appearance. Contains a variety of components that are identical to different tissues in the body, usually fat and hair. When small does not cause symptoms. It, too, can rupture and cause intra-abdominal bleeding, or cause ovarian torsion.
Endometrioma
A cyst of endometriosis in the ovary (see endometriosis). A cyst formed by cells identical to the endometrial cells, which bleed into ovarian tissue and eventually form a cystic structure that contains old blood, which looks like liquid chocolate. The endometrioma is usually part of endometriosis, and other lesions will be found in the pelvis. The endometrioma may also rupture and cause abdominal bleeding, or cause ovarian torsion, causing pain. Most of the pain in endometriosis is caused by the other lesions rather than the endometrioma.
Polycystic ovaries
A condition that is not actually a cyst, but a proliferation of multiple enlarged follicles in the ovaries. The condition does not require treatment on its own, but it may be necessary to treat symptoms of the condition, such as irregular cycles, excess hair growth, acne, obesity and infertility (see polycystic ovarian syndrome).
Malignant cysts
It is suspected that the cyst is malignant, especially when it occurs at the age before puberty or after menopause or contains suspicious characteristics such as rapid growth, different content, uneven texture and structure, irregular blood flow, additional pelvic or abdominal findings, elevated blood tumour markers.
In any case of a cyst suspected of malignancy, the woman will undergo a complete assessment including ultrasound by an expert, blood tests, and possibly CT, and early surgical intervention is recommended, usually by a gynecologist.
FAQs
What does ovarian cyst pain feel like?
An ovarian cyst can cause a few types of pain: Sharp severe pain from ovarian torsion, constant dull pain from stretching the ovary, pressure sensation if it is a large cyst pressing on the bowel, bladder or other organs.
What does an ovarian cyst feel like?
In most cases, the woman will not even know about the existence of the cyst. But, in some situations, even a benign cyst can cause pain, stress, and changes in the menstrual cycle. In addition, a cyst can cause various complications, such as when it ruptures and causes its contents to be spilled into the abdominal cavity, or twists the ovary, blocking its blood supply and possible loss of the ovary (ovarian torsion).
How long does ruptured ovarian cyst pain last?
The pain of ovarian rupture is a short acute and severe pain, but depends on the cyst’s content or if it is bleeding which will make it last longer. The following pain after the initial rupture will be a sensation of lower or all abdominal pain, bloating, pressure (on bowel or bladder), can cause diarrhoea or fainting. This can last even a couple of days.
How to get rid of ovarian cyst?
Functional cysts can be treated and resolve by using the contraception pill. Getting rid of other cysts is only by surgery. The need for surgical treatment of the cyst will be determined according to: symptoms (abdominal pain, pressure on the abdominal organs, etc.), cyst type, cyst size and growth, woman’s age, risk factors in the background and other findings in the abdomen and pelvic, and the blood tumor markers.
Most surgeries for ovarian cysts are performed in a laparoscopic approach (keyhole surgery), which are relatively easy with rapid recovery.

